Input specification via Transformation Graph Interface
We support pipelines for registering several datasets to each other, and reconstructing data from one dataset in the space of any other dataset. All of the registrations and reconstructions can be performed by executing a single command from the command line with one input, a json file which contains the following information:
Names of spaces
Registrations are computed between pairs of spaces. Each space should be given a unique name. (e.g. “atlas”, “CT”, “exvivoMRI”,”invivoMRI”, “Histology”).
Names of images
Each space may have more than one imaging dataset sampled in it (for example multiple MRI scans with different contrasts). Each image within a space should be given a unique name. (e.g. “exvivoMRI -> T1”, “exvivoMRI -> T2”, “invivoMRI -> T1”, “Histology”)
Filenames
Each image should have a filename (for 3D data), or a directory (for 2D data) associated with it.
Registration tuples
To register a complex multimodal dataset, we specify a list of (space/image to map from, space/image to map to ) tuples. These correspond to edges in a graph and should span the set of spaces. This set of transformations will be computed using our optimization procedure.
Registration Configurations
Each registration is computed using unique parameters specified in a registration configuration json file whose path must be listed. These will be loaded into python into a dictionary, which will be passed to functions via keyword arguments. Each registration is run in a multi scale fashion, from low resolution to high resolution, and so each parameter should be specified as a list (one entry for each resolution) or a singleton list (one entry for all resolutions). We have included examples of registration config files in the examples folder.
Reconstruction tuples
After transformations are computed, we can reconstruct data from one space in any other space. Tuples of the form (space/image to map from, space to map to) are specified. Given the registration tuples, a path of transformations will be computed, which may involve the composition of more than one calculated transform. We can also choose to reconstruct each image in every other space instead of specifying each mapping with a tuple.
Example
For example we can run registration and reconstruction with the command:
python transformation_graph.py --infile INPUT_JSON_FILE
Where the input json file contains:
{
"space_image_path": [["MRI", "masked", "/home/brysongray/data/MD816_mini/HR_NIHxCSHL_50um_14T_M1_masked.vtk"],
["CCF", "average_template_50", "/home/brysongray/data/MD816_mini/average_template_50.vtk"],
["MRI", "unmasked", "/home/brysongray/data/MD816_mini/HR_NIHxCSHL_50um_14T_M1.vtk"],
["CT", "masked", "/home/brysongray/data/MD816_mini/ct_mask.vtk"],
["HIST", "nissl", "/home/brysongray/data/MD816_mini/MD816_STIF_mini"]],
"registrations": [[["MRI", "masked"], ["HIST", "nissl"] ],
[ ["CCF", "average_template_50"], ["MRI", "masked"],],
[["CT", "masked"], ["MRI", "masked"] ]],
"configs": ["/home/brysongray/emlddmm/config787small.json",
"/home/brysongray/emlddmm/configMD816_MR_to_CCF.json",
"/home/brysongray/emlddmm/configMD816_MR_to_CT.json"],
"output": "/home/brysongray/emlddmm/transformation_graph_outputs",
"transforms": [[["CCF", "average_template_50"], ["HIST", "nissl"] ],
[["CT", "masked"], ["MRI", "masked"] ]],
"transform_all": "False"
}
This input structure will do the following:
It will define 4 spaces, called MRI, CCF, CT and HIST
It will define images in these spaces. Paths to images are provided.
Two images in the MRI space, called “masked” and “unmasked”.
It will define one image in CCF space called “average_template_50”.
It will define one image in CT space called “masked”.
It will define one image set in HIST space, called “nissl”.
It will define a set of registrations to calculate. Each registration requires a pair of spaces, and an image name within that space.
It will registered the masked MRI to the histology.
It will register the CCF atlas to the masked MRI
It will register the masked CT to the masked MRI
Each registration will be calculated in order, using the config files provided for parameters.
Outputs of the registration processes will be saved in the specified output directory.
Calculated transforms are applied to map images into new spaces
The average template is mapped into the HIST space
The masked CT images is mapped into the MRI space.
Generally we reconstrct all images in all spaces, in which case transform_all is set to true.
The registration procedure internally sets up the following graph
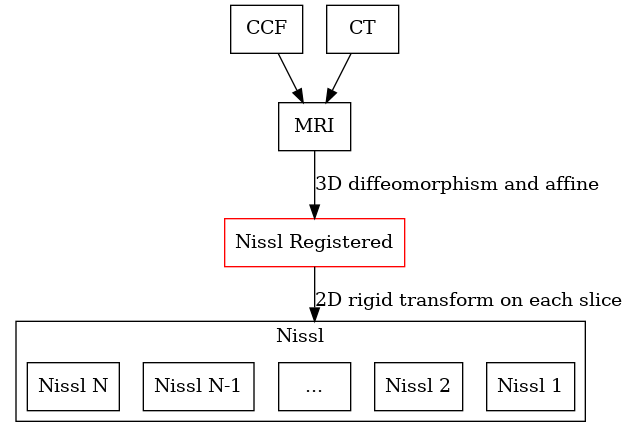
For any 3D to 2D map, a registered space is automatically created (shown in red). No input data is associated with this space, but images can be reconstructed into this space.